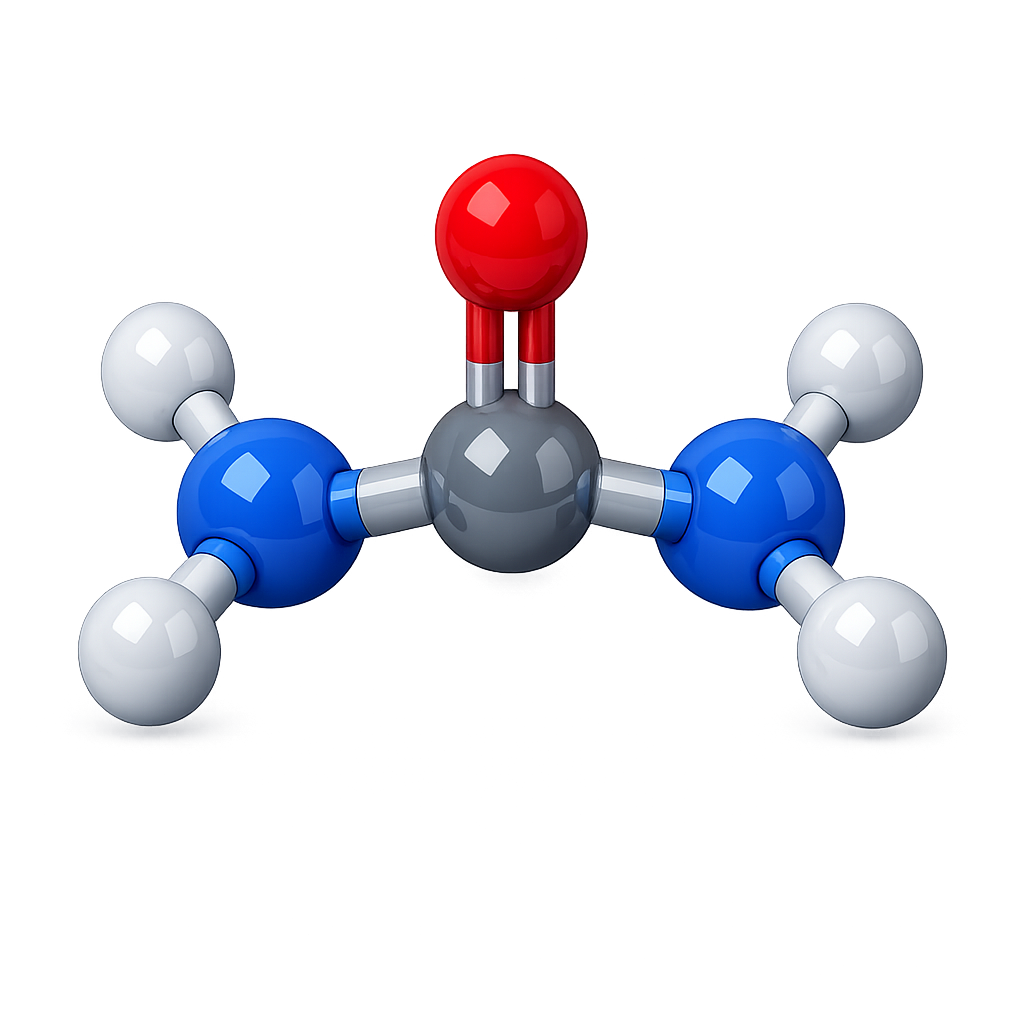
Urea
Urea is a chemical compound with the formula CO(NH₂)₂. It is a colorless, odorless, and highly soluble solid. It is also widely used in agriculture and industry. In fertilizers, it provides plants with nitrogen, an essential nutrient for their growth.
Automotive-grade urea, also known as diesel exhaust fluid (DEF), is a high-purity solution of 32.5% urea and 67.5% deionized water. It is primarily used in Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) systems in diesel vehicles, especially those with newer, more environmentally friendly engines.
Cement
Cement is a finely ground powder, is primarily made from limestone, clay, shells, and silica. When mixed with water, it undergoes a chemical reaction called hydration, which makes it harden and gain strength.
Cement is graded based on its compressive strength (measured in megapascals or MPa) at 28 days of curing. The grades are:
32.5 Grade Cement (general, construction),
42.5 Grade Cement (residential buildings),
52.5 Grade Cement (bridges, high-rise buildings)

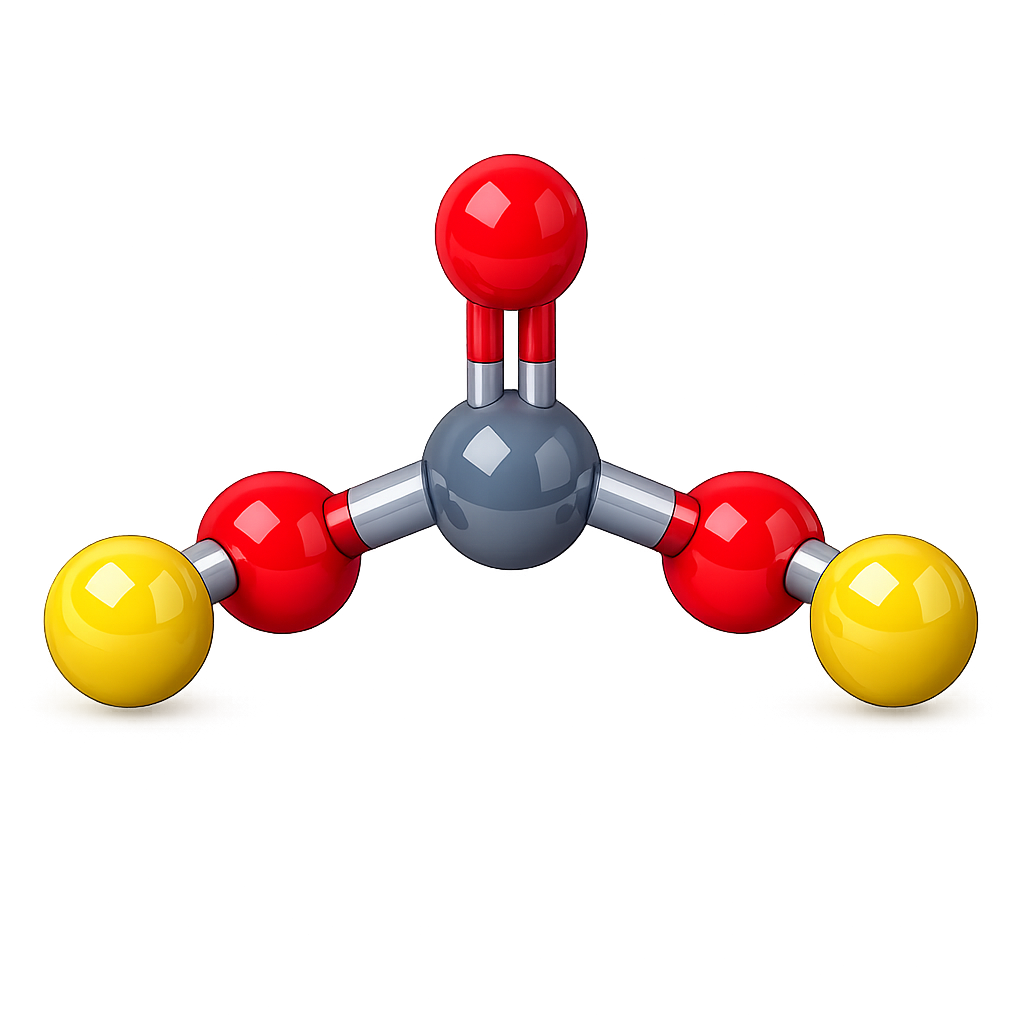
![Phosphoric Acid [H₃PO₄], Orthophosphoric Acid, Monophosphoric Acid](https://siddhi-enterprise.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/Phosphoric-Acid-H₃PO₄-1-1024x1024.png)
![Sodium chloride [NaCl]](https://siddhi-enterprise.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/Sodium-chloride-NaCl.png)
![Calcium Chloride [CaCl₂], Calcium dichloride, Anhydrous calcium chloride, Food additive number - E509](https://siddhi-enterprise.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/Calcium-Chloride-CaCl₂-1.png)
![Aluminum Sulfate [Al₂(SO₄)₃], Aluminum Sulphate [Al₂(SO₄)₃], Alum, Filter alum](https://siddhi-enterprise.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/Aluminum-Sulfate-Al₂SO₄₃-1024x1024.png)
![Magnesium Chloride [MgCl₂], Magnesium dichloride, Magnesium (II) chloride, Chloromagnesite, Magnesium chloride hexahydrate](https://siddhi-enterprise.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/Magnesium-Chloride-MgCl₂.png)
![Citric Acid [C₆H₈O₇], Lemon salt, E330, 2-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylic acid, Natural preservative](https://siddhi-enterprise.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/Citric-Acid-C₆H₈O₇.png)